ICU

Stay ahead of critical moments
In the ICU, you're there at patients' most vulnerable moments, monitoring every change in condition. The rapidly changing and complex nature of the critically ill requires continuous information to help guide the patient through the continuum of care. Advanced hemodynamic monitoring can aid you in the treatment of patients by providing information during the course of critical illness.
Hypotension management
Hypotension is a significant contributor to myocardial injury and the development of acute kidney injury (AKI) in the ICU. Studies suggest that up to 36% of patients in the ICU develop AKI. Correcting arterial hypotension is essential to restore blood pressure and provide adequate cellular metabolism, which is the primary goal of resuscitation.1,2

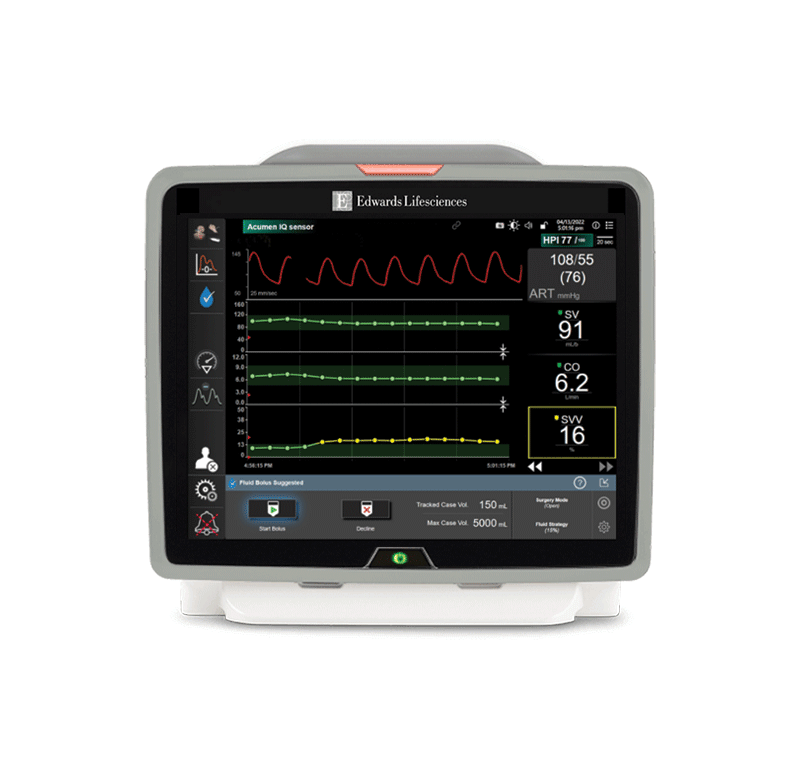
The Acumen Hypotension Prediction Index (HPI) software
The first-of-its-kind predictive decision support software that detects the likelihood of a patient trending towards a hypotensive event* before the event occurs, and provides you with insights to understand the root cause and inform a potential course of action for your patient.
*A hypotensive event is defined as mean arterial pressure (MAP) <65 mmHg for at least one minute
Perfusion optimization
Advanced hemodynamic parameters provide access to continuous pressure and flow parameters providing valuable insight into the adequacy of perfusion. Dynamic parameters can help identify the most appropriate initial therapy, such as helping you decide between volume administration versus initiation of vasopressors.
Note: Review monitoring system manual for technology compatibility


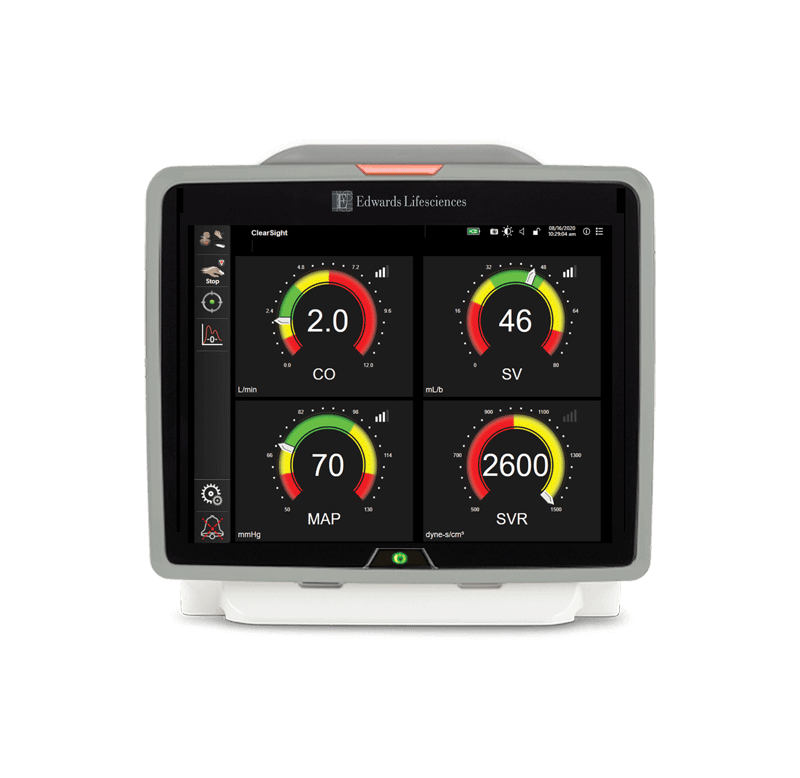
ClearSight system
Provides advanced hemodynamic parameters and continuous noninvasive blood pressure (BP) from a finger cuff. For patients in which the balance between cardiac function, fluid status and vascular resistance needs continuous assessment as well as patients with co-morbidities for which hemodynamic optimization is desired and invasive measurements are difficult.
CO | SV | SVV | SVR | SYS/DIA/MAP
Tissue oximetry management
Tissue oxygen (StO2) desaturation events are not uncommon in the cardiac and surgical ICU's. For the most critically ill patients requiring extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), tissue oximetry monitoring may help allow early identification of cerebral desaturations and limb ischemia.3

ForeSight Elite tissue oximetry system
ForeSight Elite sensors deliver accurate performance and precision in tissue oximetry. The system incorporates exclusive technology to project near infrared light in five precise wave wavelengths. A highly accurate, precise, and tailorable tissue oximetry system for continuous monitoring.
StO2
Sepsis and shock management
Shock is common. 1/3 of ICU patients suffer some form of shock.4 ICU patients presenting with shock have a nearly 40% risk of death.4 Hemodynamic measurements, like those provided by the ClearSight system, the FloTrac sensor, or the Swan-Ganz catheter working with an advanced monitoring platform, can provide clinical insight into a patient’s cardiovascular function to guide decision-making.


ClearSight system
Allows continuous assessment of your patient's physiological needs, to help you recognize sepsis and determine fluid responsiveness. The ClearSight system is a simple noninvasive technology that connects quickly to the patient over the finger and provides continuous real-time advanced hemodynamic information.
CO | SV | SVV | SVR | SYS/DIA/MAP
Pressure monitoring and blood conservation
You can make a difference in your patients’ outcomes by incorporating evidence-based closed blood sampling (CBS) procedures into your hospital’s patient blood management program. CBS is demonstrated to more effectively conserve blood, improve patient outcomes and reduce costs when compared with conventional blood sampling procedures.5-8
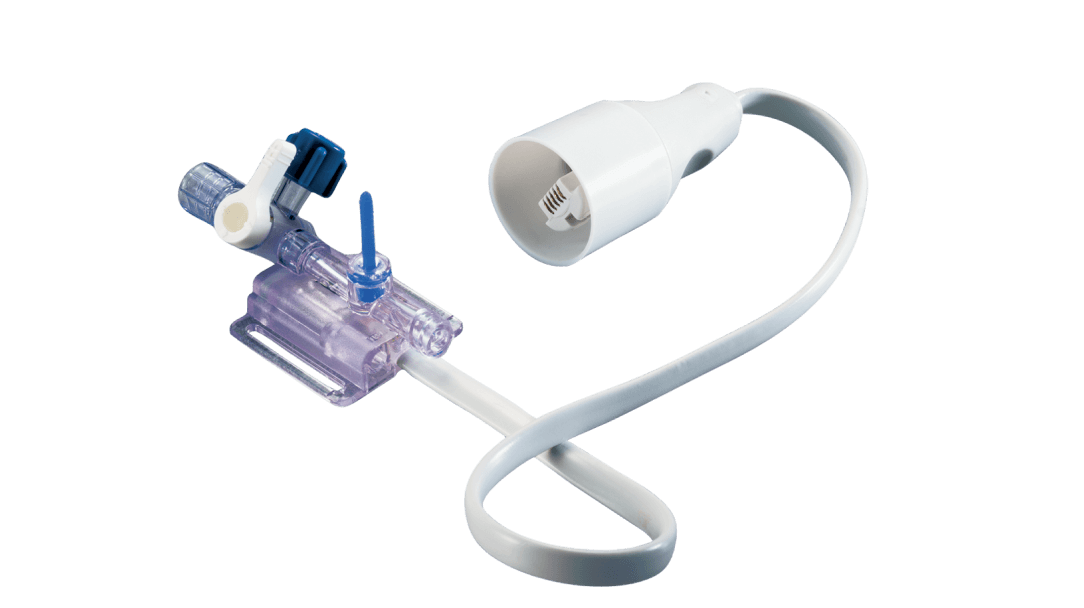


TruWave disposable pressure transducers
(adult, pediatric and flushless transducers)
Accurate and safe pressure monitoring, TruWave disposable pressure transducers may be used independently or combined with VAMP closed blood sampling systems for a single, safe, reliable and accurate monitoring solution.
References
- Lehman, L., Saeed, M., Moody, G., Mark, R., (2010) Hypotension as a Risk Factor for Acute Kidney Injury in ICU Patients. Computing in Cardiology, 37: 1095-1098.
- Maheshwari, K., et al. The relationship between ICU hypotension and in-hospital mortality and morbidity in septic patients. Intensive Care Med, 2018.
- Steffen, et al. Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy to Monitor Lower Extremities in Patients on Venoarterial Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Annals of Thoracic Surgery (2014)
- Sakr Y, Reinhart K, Vincent JL, et al. Does dopamine administration in shock influence outcome? Results of the Sepsis Occurrence in Acutely Ill Patients (SOAP) Study. Crit Care Med 2006. 589 – 597.
- Peruzzi, W.T., et al. A clinical evaluation of a blood conservation device in medical intensive care unit patients. Critical care medicine, 1993. 21 (4): p. 501-6
- Oto, J., et al., Comparison of bacterial contamination of blood conservation system and stopcock system arterial sampling lines used in critically ill patients. American Journal of Infection Control, 2012. 40(6): p.530-4
- O'Hare, D. and R.J. Chilvers, Arterial blood sampling practices in intensive care units in England and Wales. Anaesthesia, 2001. 56(6): p. 568-71
- Tang, M., et al. Closed Blood Conservation Device for Reducing Catheter-Related Infections in Children After Cardiac Surgery. Critical Care Nurse, 2014. 34(5); p.53-61
Medical device for professional use
For a listing of indications, contraindications, precautions, warnings, and potential adverse events, please refer to the Instructions for Use (consult eifu.edwards.com where applicable).