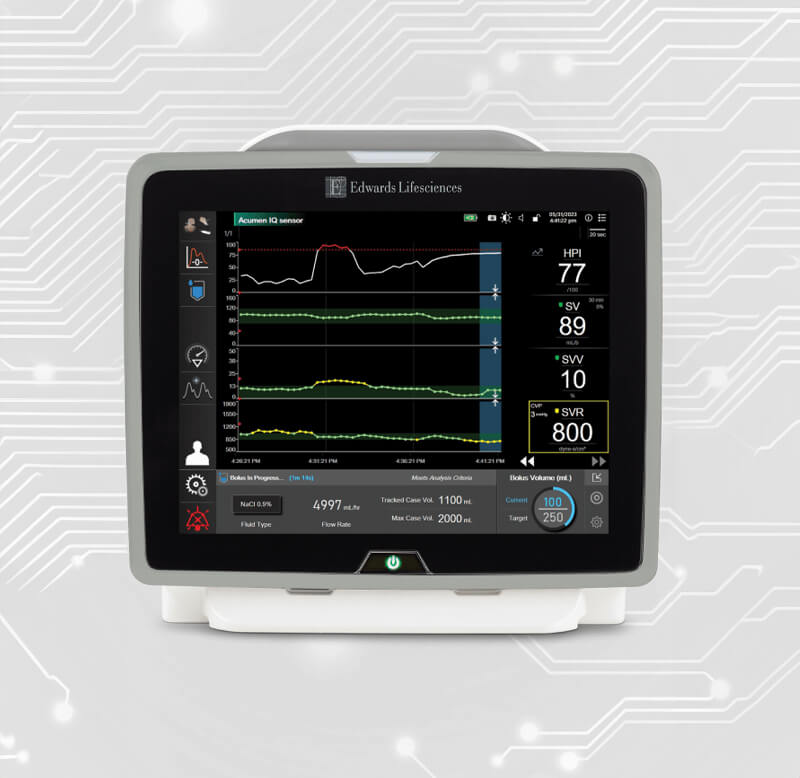
Insufficient
- GI dysfunction (postoperative ileus, PONV, anastomotic leak)6
- Infectious complication (tissue hypoperfusion)6,7
- Acute renal insufficiency or failure8
Optimise fluid administration with advanced haemodynamic parameters

Fluid management is key to ensuring adequate intraoperative pressure and flow. Both insufficient and excessive fluid administration put patients at risk of dangerous complications.1–4 However, differences in patients’ underlying needs and unique physiology can pose challenges to optimising fluid administration.5
Sufficient perfusion requires adequate arterial pressure and cardiac output (CO). Maintaining these parameters in the optimal range is key to maintaining adequate perfusion.


Both insufficient and excessive volume load can result in dangerous complications.1–4

Variability exists in fluid administration practices, with 50% of patients outside the normal fluid range.14
Physiological variability between patients increases the complexity of fluid management and can be a barrier to fluid optimisation. Fluid responsiveness can vary by fluid type, volume, infusion time and consequent change in stroke volume – and only half of haemodynamically unstable patients are fluid responsive.5
Clinician as predictor of fluid variability
While patient physiology is one factor behind fluid variability, research shows a level of fluid variability between procedures that cannot be explained by these differences alone. One study showed that the top predictor of infusion volume was the attending clinician, suggesting that protocolisation can help reduce fluid variability.14

Dynamic and flow-based parameters enable an individualised approach to fluid administration.9
The advanced parameter SV can be optimised using the patient’s own Frank-Starling curve – a plot of SV vs. preload. SV is ideal when it resides at the shoulder of the Frank-Starling curve.

SV and SVV may help clinicians:
Protocolised fluid management uses cardiac output monitoring to optimise volume status and avoid perioperative hypotension.
However, the complex and intensive nature of individualised protocols often prevent clinicians from using them as frequently as they would prefer.15–17

In the above analysis of corrected crystalloid infusion rates at two institutions,
50% of patients received rates far above or below the median.
UCI has a specific protocol for crystalloid administration during prostatectomies,
and this group had the smallest range of any of the analysed procedures,
suggesting that directed protocols can be effective in reducing variability.14

In the above analysis of corrected crystalloid infusion rates at two institutions,
50% of patients received rates far above or below the median.
UCI has a specific protocol for crystalloid administration during prostatectomies,
and this group had the smallest range of any of the analysed procedures,
suggesting that directed protocols can be effective in reducing variability.14
Acumen AFM software lessens the clinical burden of – and improves adherence to – protocols by automating patient tracking to ensure optimal fluid range.15,17
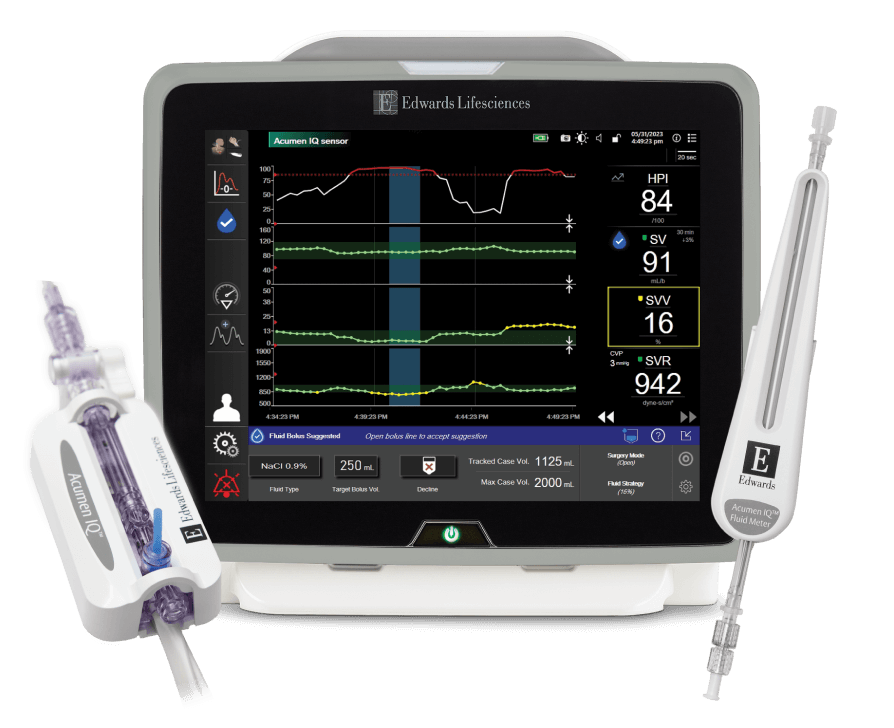

Acumen AFM software uses an algorithm to make individualised fluid recommendations based on a patient’s haemodynamic data and past responses to fluid administration, simplifying protocolisation so you can optimise fluid administration.
Acumen AFM software recommends boluses based on a machine learning algorithm that anticipates a change in a patient's SV response to fluid
Throughout a procedure Acumen AFM software adapts to your patient by using their haemodynamic data and past responses to each bolus administered
Automatically tracks volume administration and flow rate in real time* – helping you maintain a fluid strategy
*When used with Acumen IQ fluid meter and Acumen AFM cable
Dive deeper into fluid management resources – and make the most of haemodynamic monitoring technology – with our extensive clinical education library.
Thacker et al, 2015
Annals of Surger
Based on current practice of fluid use in US hospitals, Thacker et al conclude that fluid optimisation can decrease variability and improve outcomes.
Cannesson, 2010
Journal of Cardiothoracic Vascular Anesthesiology
Despite evidence that cardiac output optimisation can improve outcomes, it is rarely used in anesthesiology practice, with clinicians relying instead on qualitative methods.
Maheshwari et al, 2021
Anesthesiology
In this multicenter, prospective, single-arm cohort evaluation, fluid boluses recommended by Acumen AFM software resulted in desired SV increase more often than clinician-initiated boluses.
For a listing of indications, contraindications, precautions, warnings, and potential adverse events, please refer to the Instructions for Use (consult eifu.edwards.com where applicable).
We are committed to providing your institution, clinicians and staff with the highest levels of customer service and support to ensure seamless product implementation and ongoing use, including:
Monday through Friday, 8:00am to 17:00pm CET